How To Create More Material Slots 3ds Max

Tip1: Remember that with Mental Ray the fake reflection is NOT visible in the material slot as preview. You must make a test rendering to see the result. Tip 2: There are many ways to create Chrome. Another way to create Chrome is trough a RAYTRACE material (change standard with RAYTRACE in a new material slot). Tip 2: There are many ways to create Chrome. Another way to create Chrome is trough a RAYTRACE material (change standard with RAYTRACE in a new material slot). But the result is the same as in the standard material. Tip 3: A HDRI image can also used as a fake reflection. HDRI renderings will be explained in other Florence Design Academy. ADD TO COLLECTION. This button displays the Material Editor Options dialog to let help you control how materials and maps are displayed in the sample slots. (Material Editor): Compact (Material Editor Options) Compact Material Editor menu bar Options menu Options. These settings are “sticky”; they survive a reset, and even quitting and restarting 3ds Max. Lets you specify a custom background for the sample slots, instead of the default checkers background. Click the file-assignment button to display a file dialog from which you can select the custom background. This can be any bitmap format supported by 3ds Max.
Welcome to V-Ray for 3ds Max’s official Courseware site. The goal of this courseware is to improve the level of knowledge of V-Ray among its users.
Downloading the scenes and assets for this courseware requires a free Chaos Group account.

Courseware Highlights
- Modular: All the essential V-Ray knowledge is divided into modules to easily fit different types of curriculum.
- Easy to learn and use: Users have all materials in a ready to teach, learn and use format.
- Quality: Our curriculum has been developed with professionals and educators around the world to ensure we’re up to date with cutting edge trends in visualization.
- All training needs: Each lesson includes lectures, lesson plans, handouts, demonstration tutorials, scenes, assets, and practice assignments.
- Designed for adult learners: Based on the proven concept of learning cycles, which splits each lesson into lecture, demonstration and activity.
- Creative control: We’ve done all the hard work of creating a curriculum, so educators and users can focus on teaching, learning and artistry.
- The industry standard: Top studios around the world rely on V-Ray every day to visualize world-class products, buildings and visual effects. Students will learn industry standard skills to kick-start their careers.
Content Overview
The courseware is based on the concept of learning cycles, a proven method for teaching adults. This concept splits each topic into three distinct cycles:
- Lecture – This introduces the theory of the topic. This is the time to show imagery, discuss theories, make the connection between CG and the real world, and explain what settings do.
- Demonstration – Topics discussed in the lecture are put into action by the educator. It is important that students do not try to copy what is being shown so they can pay full attention to the demonstration and explanations.
- Activity – Students gain vital hands-on experience be reproducing what they have seen, and can do their own experiments. This cycle gives the students the chance to try out settings, solve problems, and ask questions.
The courseware provides you with materials for each of the three cycles for every Topic:
- Lecture – This includes a PowerPoint presentation, and a sample lesson plan to help your preparations.
- Demonstration and Activity – We provide you with 3ds Max scenes, and Lesson guides. Lesson guides include a sample exercise sequence for the demonstration, and they can be distributed to students. The PowerPoint presentations and Lesson guides can be downloaded separately from the page for each lesson as well as in the Download section of this courseware.
Scenes and assets are packed into a project file. These must be downloaded together to ensure that all textures and other assets will load correctly.
Topics covered by the courseware
UI & VFB
The lessons in this category provide an overview of V-Ray’s components, what they do, and where to find them in the interface.
- User Interface – A guide to the most commonly used V-Ray components
- Frame Buffer – What the V-Ray Frame Buffer is, and its most useful features
Render Engines
This section covers the two main rendering engines of V-Ray.
- V-Ray RT – How to use V-Ray RT as an ActiveShade renderer, and how to set it up to render animations.
- V-Ray Production – An overview of the standard V-Ray rendering engine, and how to use it.
Sampling
- Sampling – An in depth explanation of how to optimize antialiasing and render times.
Lighting
- V-Ray Light – The most commonly used settings of the V-Ray Light.
- V-Ray and 3ds Max Lights – How to use the Standard 3ds Max Lights with V-Ray.
- V-Ray Ambient Light – An overview of the settings of the V-Ray Ambient Light.
- V-Ray Dome Light – The workflow to generate Image Based Lighting with the V-Ray Dome Light.
- V-Ray IES Light – How light profiles and V-Ray’s IES light can create realistic lighting.
- V-Ray Sun and Sky System - Set up day time illumination with the V-Ray’s Sun and Sky system.
Global Illumination
- GI Introduction. The theory of tracing global illumination, and the technical differences between the different GI Engines in V-Ray.
- GI for Exterior Scenes – The workflow for setting up GI for Exterior Scenes.
- GI for Interior Scenes – The workflow for setting up GI for Interior Scenes.
- Caustics – How to generate sharp photon mapped caustics.
- GI for Fly-Through Animations – Optimize the rendering of fly-through animations.
Camera
- Physical Camera – Physical Camera settings, and how they affect the exposure of the rendered image.
- Physical Camera: Motion Blur and Depth of Field – How to use Motion Blur and Depth of Field effects, and how to balance the exposure of the rendered image.
Shading
- V-Ray Material – V-Ray material settings, and how to use them to simulate a wide range of real world materials.
- V-Ray SSS Materials – V-Ray FastSSS2 and V-Ray Skin materials, and how to use them tocreate translucent or sub-surface scattering materials.
- V-Ray 2-Sided Material – V-Ray 2-Sided material, and how to use it to create thin translucent materials such as fabric or paper.
- V-Ray Blend and Bump Materials – How to create more complex materials.
- Random Color Techniques – How the V-Ray Multi Sub texture and the V-Ray User Color node can generate random colors in a shading network.
Volumetrics
How To Create More Material Slots 3ds Max Online
- Volumetrics – V-Ray Aerial Perspective and V-Ray Environment Fog atmospheric effects in an exterior scene
Dynamic Geometry
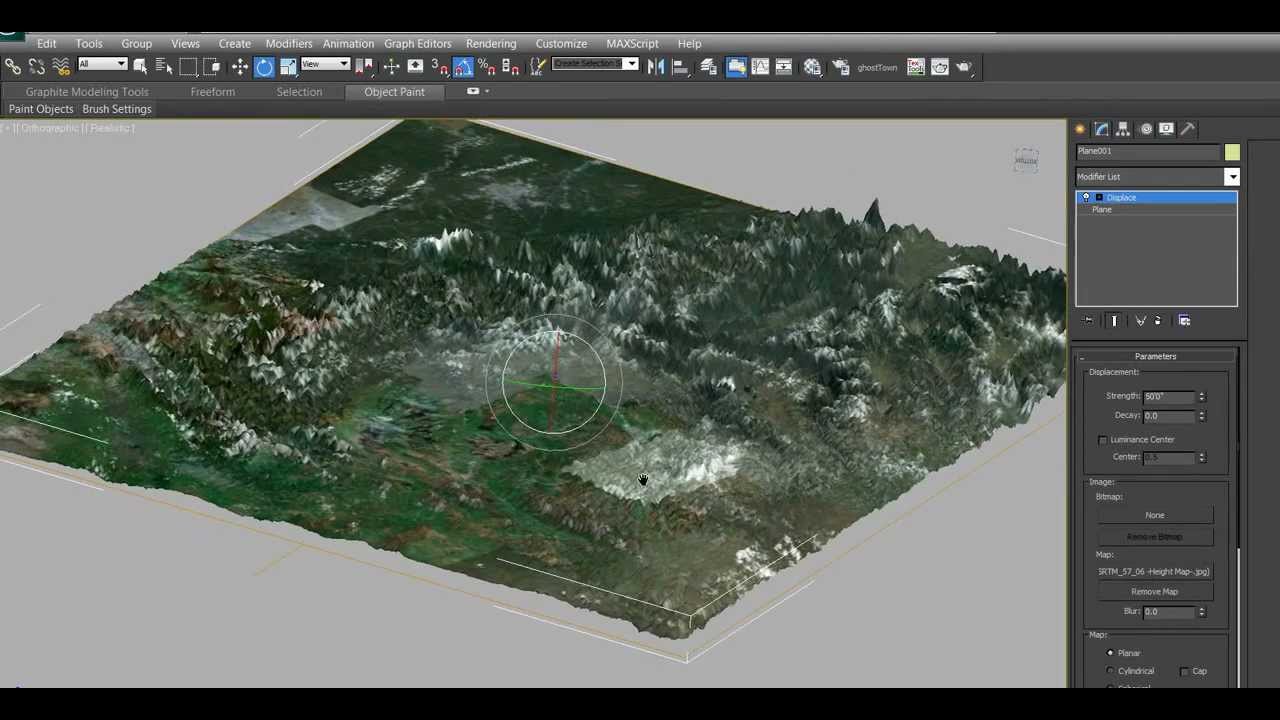
- V-Ray Displacement – Adding fine detail to scenes with the V-Ray Displacement Modifier.
- V-Ray Proxy – Optimize high poly count scenes with V-Ray’s Proxy geometry.
- V-Ray Instancer – Instance multiple V-Ray Proxy geometries with the help of a ParticleFlow system and the V-Ray Instancer helper.
- V-Ray Fur – Generate realistic grass with V-Ray Fur.
Render Elements
- V-Ray Render Elements – How to split the rendered image into render elements, and combining them in compositing.
Scenes and assets requirements and setup
To use the scenes and assets provided you need to have 3ds Max and V-Ray 3.5 for 3ds Max installed.

To get the scenes click hereand wait for the download to complete.
Once the download completes, extract the scenes into a folder of your choice. For example: C:Coursware for V-Ray 3dsMax
Start 3ds Max 2017 and go to Application Menu > Manage > Set Project Folder:
Select the folder in which you extracted the zip file. For example: C:Coursware for V-Ray 3dsMax
Maps
Maps are bitmaps or procedural textures that are used to give color and other apparent surface characteristics ('textures') to 3D objects in Max.
There can be different types of maps. Some maps wrap images about objects, while others define areas to be modified by comparing the intensity of the pixels in the map. An example of this is a bump map. A standard bump map would be a grayscale image. When mapped onto an object, lighter colored sections would be raised to a maximum of pure white and darker sections would be indented to a minimum of black. This enables you to easily create surface textures, such as an orange rind, without having to model them.
The basic parameters of a shader like diffuse, specular, self-illumination, opacity etc. can be mapped with a bitmap or a procedural texture. Clicking on the small button in front of the color swatch can do this job. Clicking on this button opens a Material/Map Browser. When a parameter is mapped, the small button shows “M”.
Figure 5-4: Shader Basic Parameters
Mapping the diffuse parameter with a bitmap will enable the bitmap to appear around the surface of the 3d object.
The Maps rollout is where you apply maps to the various materials. To use a map, click on the Map button; this opens the Material/Map Browser where you can select the map to be used. The Amount spinner sets the intensity of the map, and an option to enable or disable the map is available. For example, a white material with a red Diffuse map set at 50 % Intensity results in a pink material.
Figure 5-5: Maps Rollout
The available maps in the Maps rollout depend on the type of material and the Shader that you are using. Raytrace materials have many more available maps than the standard material. Some of the common mapping types found in the Maps rollout are discussed in this section.
Material/Map Browser
The Material/Map Browser lets you choose a material or a map. When you click Get Material, the Browser that is displayed is modeless (you can leave it displayed while you do other work). However, when you display the Browser by clicking the Type button, a map assignment button in the Environment dialog, or from a projector light (see Advanced Effects Rollout), it appears as a modal dialog with OK and Cancel buttons.
The Material/Map Browser includes several browse options accessible as radio buttons on the left of the dialog box. The browse options include Material Library, MaterialEditor, Active Slot, Selected, Scene, and New. In order to choose a bitmap image as a map, you click on New, and the Bitmap on the top of the list appears.
Figure 5-6: Material/Map Browser
UVW Mapping Coordinates
An object assigned a 2D mapped material (or a material that contains 2D maps) must have mapping coordinates. These coordinates specify how the map is projected onto the material, and whether it is projected as a 'decal,' or whether it is tiled or mirrored. Mapping coordinates are also known as UV or UVW coordinates. These letters refer to coordinates in the object's own space, as opposed to the XYZ coordinates that describe the scene as a whole.
Mapping coordinates are used to define how a texture map is aligned to an object. These coordinates are expressed using U, V, and W dimensions, with U being a horizontal direction, V being a vertical direction, and W being depth.
How To Make More Material Slots In 3ds Max
UVW Map Modifier:
UVW Map modifier controls how mapped and procedural materials appear on the surface of an object. Mapping coordinates specify how bitmaps are projected onto an object. The UVW coordinate system is similar to the XYZ coordinate system. The U and V axes of a bitmap correspond to the X and Y axes. The W axis, which corresponds to the Z axis, is generally only used for procedural maps. A bitmap's coordinate system can be switched in the Material Editor to VW or WU, in which case the bitmap is rotated and projected so that it is perpendicular to the surface.
How To Create More Material Slots 3ds Max Walkthrough
UVW Map Modifier projects the UVW coordinates on the surface of the 3d object. This projection can be done in the following available ways.
- Planar
- Cylindrical
- Spherical
- Shrink Wrap
- Box
- Face
- XYZ to UVW
Primitives, Loft Objects, and NURBS can generate their own mapping coordinates, but you need to use this modifier to apply mapping coordinates to mesh objects and patches.
Unwrap UVW Modifier
How To Create More Material Slots 3ds Max Games
The Unwrap UVW modifier lets you control how a map is applied to a subobject selection. It can also be used to unwrap the existing mapping coordinates of an object. You can then edit these coordinates as needed. You can also use the Unwrap UVW modifier to apply multiple planar maps to an object. You accomplish this task by creating planar maps for various sides of an object and then editing the mapping coordinates in the Edit UVWs interface.
How To Create More Material Slots 3ds Max Free
The Unwrap UVW modifier can be used as a self-contained UVW mapper and UVW coordinate editor, or in conjunction with the UVW Map modifier. If you use Unwrap UVW in conjunction with the UVW Map modifier, it is usually because you want to map the model with a method other than planar mapping, such as cylindrical or spherical mapping. You can animate UVW coordinates by turning on the Auto Key button and transforming the coordinates at different frames.